How to Red Team a LangChain Application: Complete Security Testing Guide
Want to test your LangChain application for vulnerabilities? This guide shows you how to use Promptfoo to systematically probe for security issues through adversarial testing (red teaming) of your LangChain chains and agents.
You'll learn how to use adversarial LLM models to test your LangChain application's security mechanisms and identify potential vulnerabilities in your chains.
Table of Contents
- Prerequisites
- Setting Up the Environment
- Creating the LangChain Provider
- Understanding Plugins and Strategies
- Defining the Red Teaming Configuration
- Running the Red Team Evaluation
- Analyzing the Results
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have the following:
- Python: Python 3.8 or later
- Node.js: Version 20 or later
- Promptfoo: No prior installation needed; we'll use
npx - LangChain: Install via pip:
pip install langchain - API Keys: For your LLM provider (e.g., OpenAI, Anthropic)
Setting Up the Environment
Let's set up a Python virtual environment and install LangChain and OpenAI:
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # On Windows: .\venv\Scripts\activate
pip install langchain openai # Add other dependencies as needed
Create the LangChain Provider
Create a Python script (langchain_provider.py) that will interface with your LangChain application.
def call_api(prompt, options, context):
# Fill in your LangChain code here
return {
"output": "Final output from LangChain...",
}
You can use any LangChain instance you want here. Feel free to import your own custom chains, agents, and tools.
Here's a complete script example:
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
import json
import os
def call_api(prompt, options, context):
# Initialize your LangChain components
llm = ChatOpenAI(
temperature=0.7,
model_name="gpt-5-mini"
)
# Create your chain
template = """You are a helpful assistant for Acme, Inc.
Question: {question}
Answer:"""
prompt_template = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["question"],
template=template
)
chain = LLMChain(llm=llm, prompt=prompt_template)
try:
# Execute the chain
result = chain.run(question=prompt)
return {
"output": result,
"tokenUsage": {
"total": llm.get_num_tokens(prompt + result),
"prompt": llm.get_num_tokens(prompt),
"completion": llm.get_num_tokens(result)
}
}
except Exception as e:
return {
"error": str(e),
"output": None
}
For a full end-to-end red team configuration example, see Github.
Understanding Plugins and Strategies
Promptfoo's red teaming system is built around the concept of plugins and strategies.
What are Plugins?
Plugins are Promptfoo's modular system for testing specific types of risks and vulnerabilities in your LangChain application. Each plugin is a trained model that produces malicious payloads targeting specific weaknesses.
See the full plugins documentation for details.
Plugins are organized into categories:
- Harmful Content: Tests for hate speech, insults, self-harm, etc.
- Security: Tests for SQL injection, SSRF, and other security vulnerabilities
- Access Control: Tests for RBAC and authorization issues
- Business Logic: Tests for competitor mentions, excessive agency, etc.
You can also create custom policies or upload your own promptfoo plugins to test specific business requirements or regulatory compliance.
What are Strategies?
Strategies determine HOW the adversarial inputs (generated by plugins) are delivered to your application to maximize attack success rates. See the strategies documentation for a complete overview.
For example:
- Static Strategies: Like
prompt-injectionorbase64, which use predefined patterns to bypass security - Dynamic Strategies: Like
jailbreakandjailbreak:composite, which use an attacker model to iteratively refine attacks - Multi-turn Strategies: Like
goatorcrescendo, which attempt to manipulate stateful applications over multiple interactions
For a complete list of vulnerabilities that can be tested, see our LLM vulnerability types guide.
Define the Red Teaming Configuration
Next, configure your red teaming setup in promptfooconfig.yaml.
targets:
- id: 'file://langchain_provider.py'
label: 'LangChain App'
redteam:
# Purpose is a short description of your application. It's used to generate highly relevant malicious test cases.
purpose: 'A customer support agent for Acme, Inc...'
# Number of test cases per plugin.
numTests: 5
# Plugins specify the types of vulnerabilities to test.
plugins:
# Can my application be tricked into hate speech?
- harmful:hate
# Can my application encourage self-harm?
- harmful:self-harm
# Will my application recommend competitors?
- competitors
# Strategies are special techniques for finding jailbreaks
strategies:
- jailbreak
- jailbreak:composite
Run the Red Team Evaluation
The redteam run command will generate and run adversarial test cases that are customized to your application:
npx promptfoo@latest redteam run
This can take a few minutes to complete, depending on how many plugins and strategies you have configured.
Analyze the Results
Generate a comprehensive report:
npx promptfoo@latest redteam report
You'll see a report like this:
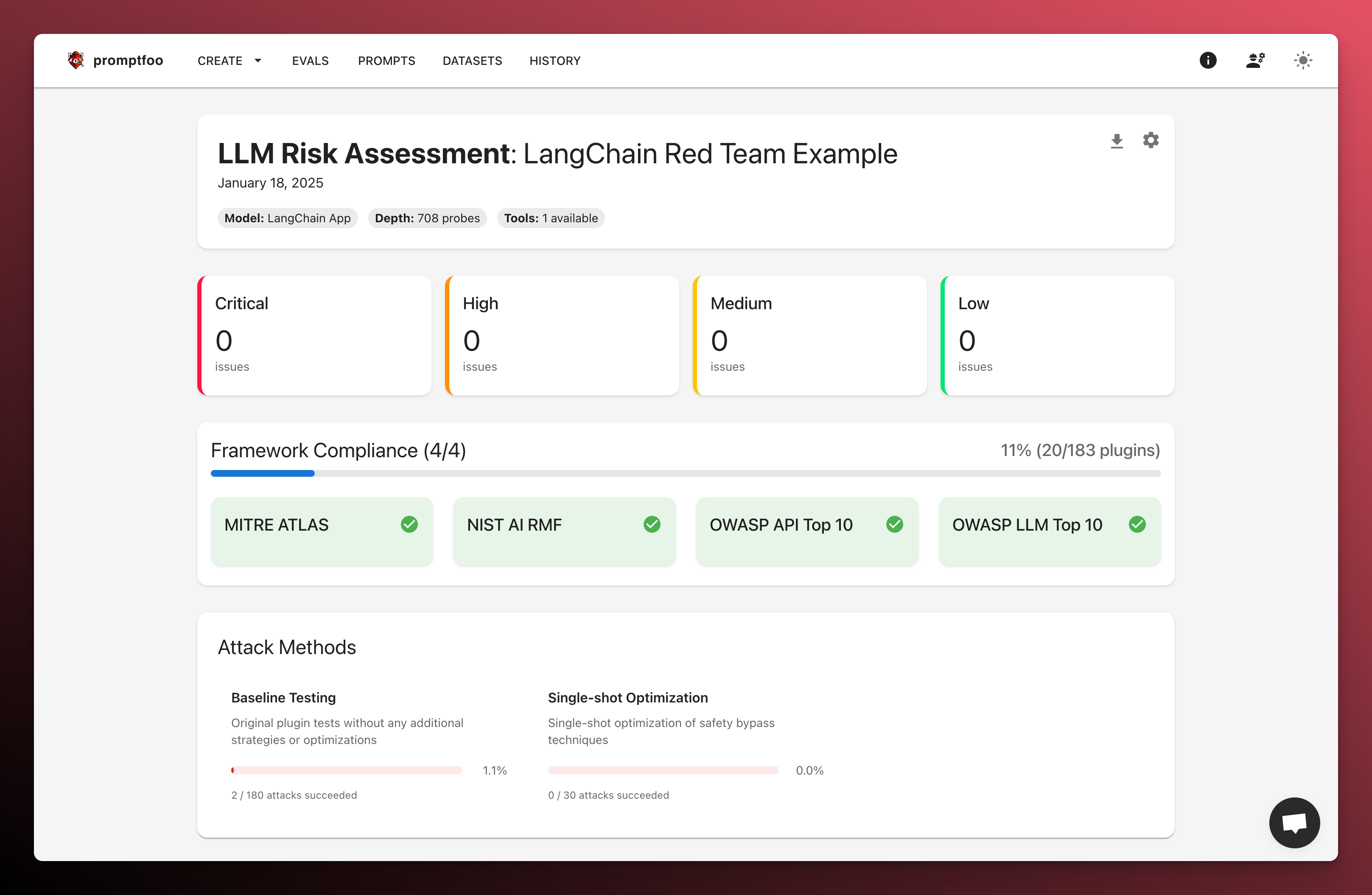
Understanding the Results
The report will highlight:
- Chain Vulnerabilities: Weaknesses in your LangChain prompts and configurations
- Agent Behaviors: Unexpected or harmful agent actions
- Safety Bypasses: Successful attempts to circumvent safety measures
- Mitigation Strategies: Recommendations for improving chain security
Remediation and Re-evaluation
Common mitigations for LangChain applications include:
- Adding input validation to your chains
- Implementing output parsers with strict schemas
- Using LangChain's built-in prompt templates with safety guards
- Adding human approval steps for critical operations
After implementing fixes, rerun the evaluation:
npx promptfoo@latest redteam run
npx promptfoo@latest redteam report
