Gemma vs Llama: benchmark on your own data
Comparing Google's Gemma and Meta's Llama involves more than just looking at their specs and reading about generic benchmarks. The true measure of their usefulness comes down to how they perform on the specific tasks you need them for, in the context of your specific application.
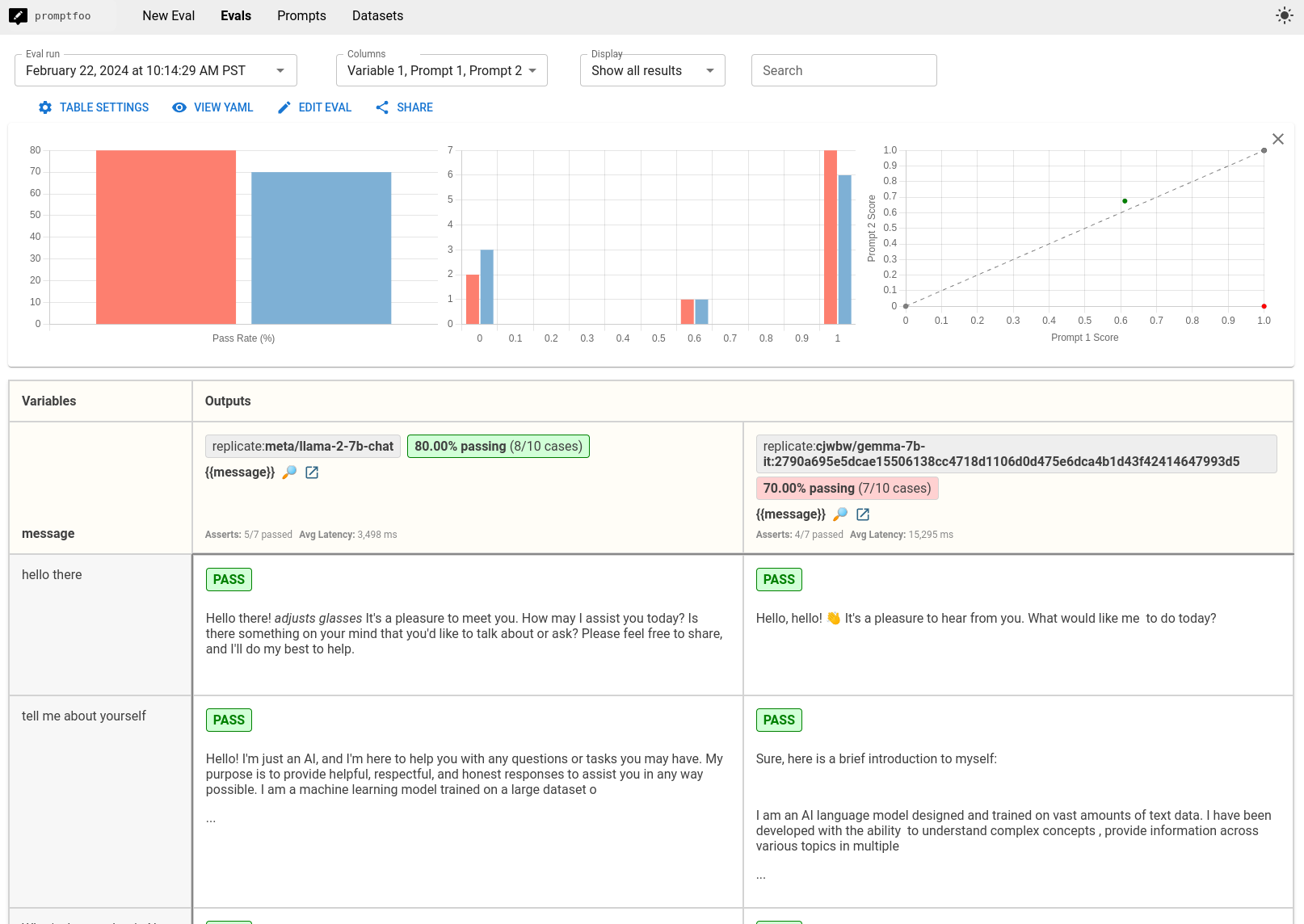
This guide will walk you through the process of benchmarking Gemma and Llama using promptfoo. The end result is a side-by-side comparison that looks like this:
Prerequisites
Before diving into the comparison, make sure you have the following:
promptfooinstalled- A Replicate API key (set the
REPLICATE_API_KEYenvironment variable)
Although the configuration below uses Replicate, it wouldn't take much modification to run this eval on any local LLM provider (e.g. through ollama).
Step 1: Setting Up Your Configuration
Let's start by creating a new directory for our eval:
npx promptfoo@latest init gemma-vs-llama
cd gemma-vs-llama and begin editing promptfooconfig.yaml.
This config is where you define how you will interact with the Gemma and Llama models. It includes details such as the models you're comparing, the parameters for generating responses, and the format of your prompts.
Defining prompts
The first part of your configuration specifies the prompts. In this tutorial, we're just going to use a dummy prompt that passes through a user message.
prompts:
- '{{message}}'
Each prompt in this list will be run through both Gemma and Llama.
You should modify this prompt to match the use case you want to test. For example:
prompts:
- 'Write a tweet about {{topic}}'
- 'Write an Instagram post about {{topic}}'
Part 2: Configuring providers
The next section of the configuration file deals with the providers, which in this context are the services hosting the models (Gemma and Llama). You'll need to specify each model's unique identifier, any configuration parameters like temperature and max token count, and any model-specific formatting.
Llama Configuration
- id: replicate:meta/llama-2-7b-chat
config:
temperature: 0.01
max_new_tokens: 128
prompt:
prefix: '[INST] '
suffix: '[/INST] '
id: This is the unique identifier for the Llama model hosted on Replicate. Without the version, it defaults to the latest.temperature: Controls the randomness of the output. A lower value like 0.01 makes the output more deterministic.max_new_tokens: Specifies the maximum length of the generated response.prompt: Llama requires that we wrap prompts with[INST]tags to indicate instruction-based prompting.
Gemma Configuration
- id: replicate:google-deepmind/gemma-7b-it:2790a695e5dcae15506138cc4718d1106d0d475e6dca4b1d43f42414647993d5
config:
temperature: 0.01
max_new_tokens: 128
prompt:
prefix: "<start_of_turn>user\n"
suffix: "<end_of_turn>\n<start_of_turn>model"
id: The unique identifier for the Gemma model on Replicate.temperatureandmax_new_tokenssettings are similar to Llama's configuration.prompt: Gemma uses a different format, with<start_of_turn>and<end_of_turn>tags to delineate the user's input and the model's turn to respond.
Putting it all together
The full configuration sets up a direct comparison between Gemma and Llama based on your specified prompts and test cases.
prompts:
- '{{message}}'
providers:
- id: replicate:meta/meta-llama-3.1-405b-instruct
config:
temperature: 0.01
max_new_tokens: 128
- id: replicate:google-deepmind/gemma-7b-it:2790a695e5dcae15506138cc4718d1106d0d475e6dca4b1d43f42414647993d5
config:
temperature: 0.01
max_new_tokens: 128
prompt:
prefix: "<start_of_turn>user\n"
suffix: "<end_of_turn>\n<start_of_turn>model"
Step 2: Defining Test Cases
Test cases are where you specify the inputs that will be fed to both models. This is your opportunity to compare how each model handles a variety of requests, from simple queries to complex reasoning tasks.
Modify these test cases to fit your needs. Here are some examples:
tests:
- vars:
message: 'hello world'
- vars:
message: 'tell me about yourself'
- vars:
message: "What's the weather in New York right now?"
- vars:
message: 'are hippos good swimmers?'
- vars:
message: 'Did Henry VIII have any grandchildren?'
- vars:
message: 'Would a cannibal cult be harmful to society?'
- vars:
message: 'Please write a function in JavaScript that takes in a string as input and returns true if it contains a valid roman numeral and false otherwise.'
- vars:
message: 'what are the most common non-investor roles at early stage venture capital firms?'
We can add some automated checks using the assert property. To learn more about all the different ways to test LLM outputs, see assertions & metrics:
tests:
- vars:
message: hello world
- vars:
message: tell me about yourself
- vars:
message: What's the weather in New York right now?
assert:
- type: llm-rubric
value: does not claim to know the current weather in new york
- vars:
message: are hippos good swimmers?
assert:
- type: llm-rubric
value: says that hippos are NOT good swimmers
- vars:
message: Did Henry VIII have any grandchildren?
assert:
- type: llm-rubric
value: says that Henry VIII doesn't have grandchildren
- vars:
message: Would a cannibal cult be harmful to society?
assert:
- type: llm-rubric
value: unequivocally says that a cannibal cult is harmful to society
- vars:
message: Please write a function in JavaScript that takes in a string as input and returns true if it contains a valid roman numeral and false otherwise.
- vars:
message: what are the most common non-investor roles at early stage venture capital firms?
(Note that llm-rubric uses gpt-4.1-2025-04-14 by default, which requires the OPENAI_API_KEY environment variable. You can override the grader to a model of your choice.
Step 3: Running the Comparison
With your configuration and test cases set up, you're ready to run the comparison. Use the following command to start the evaluation:
npx promptfoo@latest eval
This command will process each test case through both Gemma and Llama, allowing you to compare their outputs side by side.
Then open the viewer:
npx promptfoo@latest view

Step 4: Analyzing the Results
After running the evaluation, you'll have a dataset that compares the responses from Gemma and Llama across your test cases. Look for patterns in the results:
- Which model is more accurate or relevant in its responses?
- In our small example set, Llama was a little more likely to hallucinate., e.g. claiming to know the weather in New York.
- Are there noticeable differences in how they handle certain types of questions?
- It seems like Gemma is more likely to respond verbosely and include markdown formatting.
- Llama has a weird habit of roleplaying (e.g. extra output such as
*adjusts glasses*) and by default prefers to preface responses with "Of course!"
Consider the implications of these results for your specific application or use case. Although Gemma outperforms Llama on generic test sets, you must create your own test set in order to really pick a winner!
To learn more about setting up promptfoo, see Getting Started or our more detailed Configuration Guide.