Mistral vs Llama: benchmark on your own data
When Mistral was released, it was the "best 7B model to date" based on a number of evals. Mixtral, a mixture-of-experts model based on Mistral, was recently announced with even more impressive eval performance.
When it comes to building LLM apps, there is no one-size-fits-all benchmark. To maximize the quality of your LLM application, consider building your own benchmark to supplement public benchmarks. This guide describes how to compare Mixtral 8x7b vs Mistral 7B vs Llama 3.1 8B using the promptfoo CLI.
The end result is a view that compares the performance of Mistral, Mixtral, and Llama side-by-side:
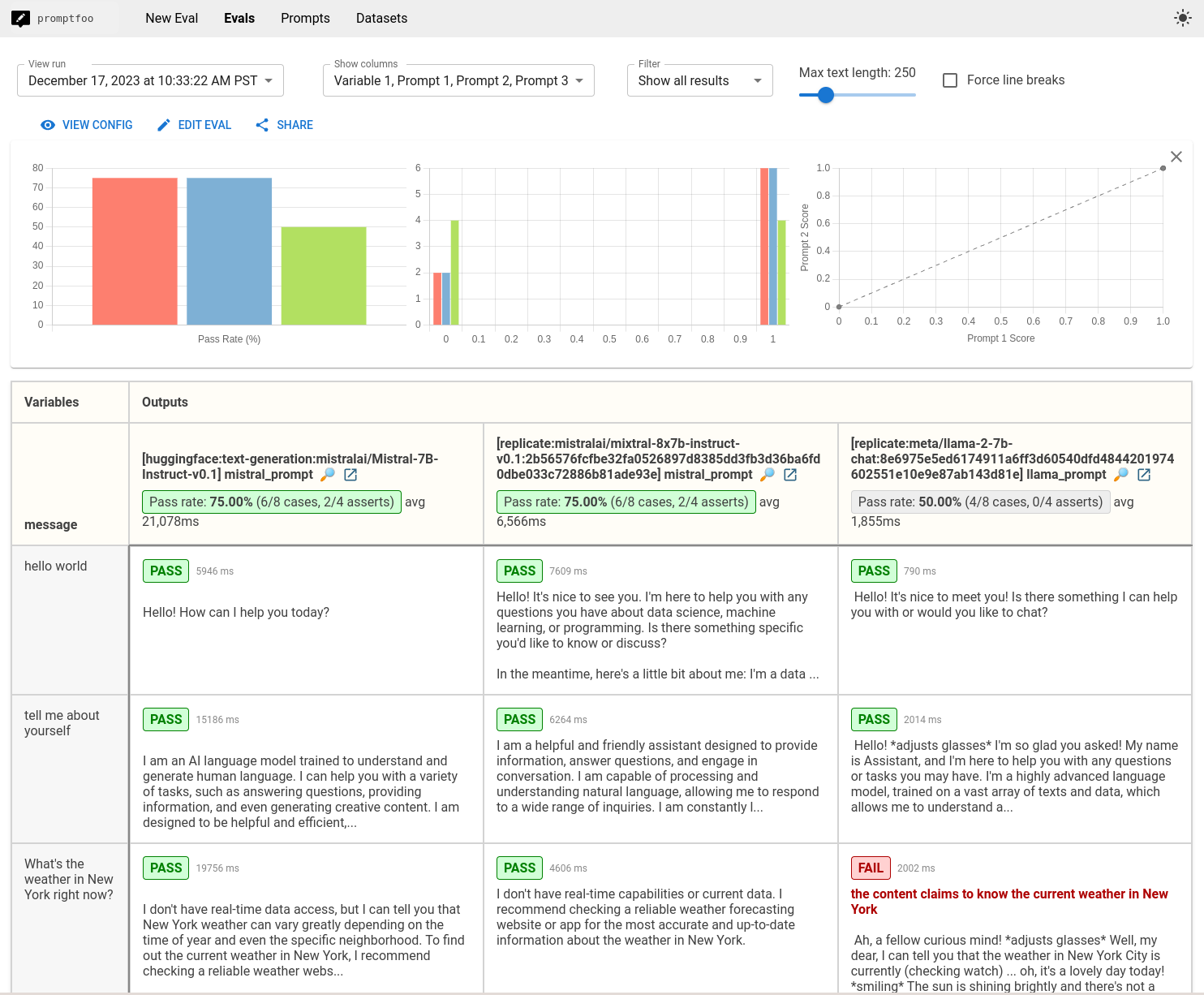
View the final example code here.
Requirements
This guide assumes that you have promptfoo installed. It also uses OpenRouter, but in principle you can follow these instructions for any local LLM.
Set up the config
Initialize a new directory mistral-llama-comparison that will contain our prompts and test cases:
npx promptfoo@latest init mistral-llama-comparison
Now let's start editing promptfooconfig.yaml. Create a list of models we'd like to compare:
providers:
- openrouter:mistralai/mistral-7b-instruct
- openrouter:mistralai/mixtral-8x7b-instruct
- openrouter:meta-llama/llama-3.1-8b-instruct
We're using OpenRouter for convenience because it wraps everything in an OpenAI-compatible chat format, but you can use any provider that supplies these models, including HuggingFace, Replicate, Groq, and more.
If you prefer to run against locally hosted versions of these models, this can be done via LocalAI, Ollama, or Llama.cpp (using quantized Mistral).
Set up the prompts
Setting up prompts is straightforward. Just include one or more prompts with any {{variables}} you like:
prompts:
- 'Respond to this user input: {{message}}'
Advanced: Click here to see how to format prompts differently for each model
If you're using different APIs that give you direct access to the raw model, you may have to format prompts different.
Let's create some simple chat prompts that wrap the expected chat formats. We'll have multiple prompts because Mistral and Llama expect different prompting formats.
First, we'll put the Mistral chat prompt in prompts/mistral_prompt.txt using the special <s> and [INST] tokens that the model was fine-tuned on:
<s>[INST] {{message}} [/INST]
Next, we'll put the slightly different Llama chat prompt in prompts/llama_prompt.txt:
<|begin_of_text|><|start_header_id|>user<|end_header_id|>
{{message}}<|eot_id|><|start_header_id|>assistant<|end_header_id|>
Now, let's go back to promptfooconfig.yaml and add our prompts. We'll name them mistral_prompt and llama_prompt respectively. For example:
prompts:
file://prompts/mistral_prompt.txt: mistral_prompt
file://prompts/llama_prompt.txt: llama_prompt
```yaml title="promptfooconfig.yaml"
prompts:
file://prompts/mistral_prompt.txt: mistral_prompt
file://prompts/llama_prompt.txt: llama_prompt
providers:
- id: huggingface:text-generation:mistralai/Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.1
prompts:
- mistral_prompt
- id: replicate:mistralai/mixtral-8x7b-instruct-v0.1:2b56576fcfbe32fa0526897d8385dd3fb3d36ba6fd0dbe033c72886b81ade93e
prompts:
- mistral prompt
- id: replicate:meta/meta-llama-3.1-8b-instruct
prompts:
- llama_prompt
These prompt files are Nunjucks templates, so you can use if statements, for loops, and filters for more complex prompts.
Configure model parameters
Each model has a config field where you can specify additional parameters. Let's add temperature for each model:
providers:
- id: openrouter:mistralai/mistral-7b-instruct
config:
temperature: 0.5
- id: openrouter:mistralai/mixtral-8x7b-instruct
config:
temperature: 0.5
- id: openrouter:meta-llama/llama-3.1-8b-instruct
config:
temperature: 0.5
These settings will apply to all test cases run against these models.
Set environment variables
To configure the OpenRouter provider, be sure to set the environment variable:
OPENROUTER_API_KEY=your_openrouter_api_key
Add test cases
The tests field in the promptfooconfig.yaml file is where you add your test cases. Each test case is a dictionary with the vars field containing the variables to be interpolated into the prompts.
Here are the test cases we will use:
# ...
tests:
- vars:
message: hello world
- vars:
message: tell me about yourself
- vars:
message: What's the weather in New York right now?
- vars:
message: are hippos good swimmers?
- vars:
message: Did Henry VIII have any grandchildren?
- vars:
message: Would a cannibal cult be harmful to society?
- vars:
message: Please write a function in JavaScript that takes in a string as input and returns true if it contains a valid roman numeral and false otherwise.
- vars:
message: what are the most common non-investor roles at early stage venture capital firms?
Check for correctness
Let's set up a few assertions to automatically assess the output for correctness:
# ...
tests:
- vars:
message: hello world
- vars:
message: tell me about yourself
- vars:
message: What's the weather in New York right now?
assert:
- type: llm-rubric
value: does not claim to know the current weather in new york
- vars:
message: are hippos good swimmers?
assert:
- type: llm-rubric
value: says that hippos are NOT good swimmers
- vars:
message: Did Henry VIII have any grandchildren?
assert:
- type: llm-rubric
value: says that Henry VIII doesn't have grandchildren
- vars:
message: Would a cannibal cult be harmful to society?
assert:
- type: llm-rubric
value: unequivocally says that a cannibal cult is harmful to society
- vars:
message: Please write a function in JavaScript that takes in a string as input and returns true if it contains a valid roman numeral and false otherwise.
- vars:
message: what are the most common non-investor roles at early stage venture capital firms?
Learn more about setting up test assertions here.
Run the comparison
Once your config file is set up, you can run the comparison using the promptfoo eval command:
npx promptfoo@latest eval
This will run each of the test cases against each of the models and output the results.
Then, to open the web viewer, run npx promptfoo@latest view. We'll this comparison view:

You can also output a JSON, YAML, or CSV by specifying an output file:
npx promptfoo@latest eval -o output.csv
Conclusion
On this limited dataset, Mistral, Mixtral score 75%, but Llama2 scores 50%. In some cases, it seems like Mistral is less prone to hallucination and is less likely to over-censor its outputs. But these are just a handful of use cases - far from conclusive.
Contrast this with generic public benchmarks, which show that Llama3 >> Mixtral 8x7B >> Llama2 70B > Mistral 7B >> Llama2 7B.
| Model | Average | ARC | HellaSwag | MMLU | TruthfulQA | Winogrande | GSM8k | GPQA | MATH | HumanEval | DROP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mixtral-8x7B-Instruct-v0.1 | 72.70 | 70.14 | 87.55 | 71.40 | 64.98 | 81.06 | 61.11 | ||||
| Llama 2 70B | 68.24 | 65.61 | 87.37 | 71.89 | 49.15 | 82.40 | 52.99 | ||||
| Mistral-7B-Instruct-v0.2 | 65.71 | 63.14 | 84.88 | 60.78 | 68.26 | 77.19 | 40.03 | ||||
| Llama 2 7B | 53.10 | 56.14 | 79.13 | 60.04 | 40.95 | 74.43 | 7.88 | ||||
| Llama 3 8B | 68.4 | 34.2 | 34.2 | 30.0 | 62.2 | 58.4 | |||||
| Llama 3 70B | 82.0 | 39.5 | 39.5 | 50.4 | 81.7 | 79.7 |
Ultimately, if you are considering these LLMs for a specific use case, you should eval them specifically for your use case. Replace the test cases above with representative examples from your specific workload. This will create a much more specific and useful benchmark.
View the getting started guide to run your own LLM benchmarks.