Sandboxed Evaluations of LLM-Generated Code
You're using LLMs to generate code snippets, functions, or even entire programs. Blindly trusting and executing this generated code in our production environments - or even in development environments - can be a severe security risk.
This is where sandboxed evaluations come in. By running LLM-generated code in a controlled, isolated environment, we can:
- Safely assess the code correctness.
- Benchmark different LLMs or prompts to find which produce the most reliable code.
- Catch potential errors, infinite loops, or resource-intensive operations before they impact the host system.
In this tutorial, we'll use promptfoo to set up an automated pipeline for generating Python code with an LLM, executing it in a secure sandbox using epicbox, and evaluating the results.
Prerequisites
Make sure you have the following installed:
- Node.js and npm
- Python 3.9+
- Docker
- promptfoo (
npm install -g promptfoo) - epicbox (
pip install epicbox) - urllib3 < 2 (
pip install 'urllib3<2')
Pull the Docker image you want to use so it is available locally. In this tutorial, we'll use a generic Python image, but you can use a custom one if you want:
docker pull python:3.9-alpine
Configuration
Create the promptfoo configuration file
Create a file named promptfooconfig.yaml:
prompts: file://code_generation_prompt.txt
providers:
- openai:gpt-5
- ollama:chat:llama3.3:70b
tests:
- vars:
problem: 'Write a Python function to calculate the factorial of a number'
function_name: 'factorial'
test_input: '5'
expected_output: '120'
- vars:
problem: 'Write a Python function to check if a string is a palindrome'
function_name: 'is_palindrome'
test_input: "'racecar'"
expected_output: 'True'
- vars:
problem: 'Write a Python function to find the largest element in a list'
function_name: 'find_largest'
test_input: '[1, 5, 3, 9, 2]'
expected_output: '9'
defaultTest:
assert:
- type: python
value: file://validate_and_run_code.py
This configuration does several important things:
- It tells promptfoo to use our prompt template
- We're testing GPT-4o and Llama 3 (you can replace this with a provider of your choice. Promptfoo supports both local and commercial providers).
- It defines coding problems. For each problem, it specifies the function name, a test input, and the expected output.
- It sets up a Python-based assertion that will run for each test case, validating the generated code.
Create the prompt template
Create a file named code_generation_prompt.txt with the following content:
You are a Python code generator. Write a Python function to solve the following problem:
{{problem}}
Use the following function name: {{function_name}}
Only provide the function code, without any explanations or additional text. Wrap your code in triple backticks.
This prompt will be sent to the LLM, with {{variables}} substituted accordingly (this prompt is a jinja-compatible template).
Set up the Python assertion script
Create a file named validate_and_run_code.py. This will be a Python assertion that dynamically grades each coding problem by running it in a Docker container using epicbox.
import epicbox
import re
# Replace with your preferred Docker image
DOCKER_IMAGE = 'python:3.9-alpine'
def get_assert(output, context):
# Extract the Python function from the LLM output
function_match = re.search(r'```python\s*\n(def\s+.*?)\n```', output, re.DOTALL)
if not function_match:
return {'pass': False, 'score': 0, 'reason': 'No function definition found'}
function_code = function_match.group(1)
epicbox.configure(
profiles=[
epicbox.Profile('python', DOCKER_IMAGE)
]
)
function_name = context['vars']['function_name']
test_input = context['vars']['test_input']
expected_output = context['vars']['expected_output']
# Create a Python script to call the LLM-written function
test_code = f"""
{function_code}
# Test the function
result = {function_name}({test_input})
print(result)
"""
files = [{'name': 'main.py', 'content': test_code.encode('utf-8')}]
limits = {'cputime': 1, 'memory': 64}
# Run it
result = epicbox.run('python', 'python main.py', files=files, limits=limits)
# Check the result
if result['exit_code'] != 0:
return {'pass': False, 'score': 0, 'reason': f"Execution error: {result['stderr'].decode('utf-8')}"}
actual_output = result['stdout'].decode('utf-8').strip()
if actual_output == str(expected_output):
return {'pass': True, 'score': 1, 'reason': f'Correct output: got {expected_output}'}
else:
return {'pass': False, 'score': 0, 'reason': f"Incorrect output. Expected: {expected_output}, Got: {actual_output}"}
Running the Evaluation
Execute the following command in your terminal:
promptfoo eval
This command will:
- Generate Python code for each problem using an LLM
- Extract the generated code
- Run it in the Docker sandbox environment
- Determine whether the output is correct or not
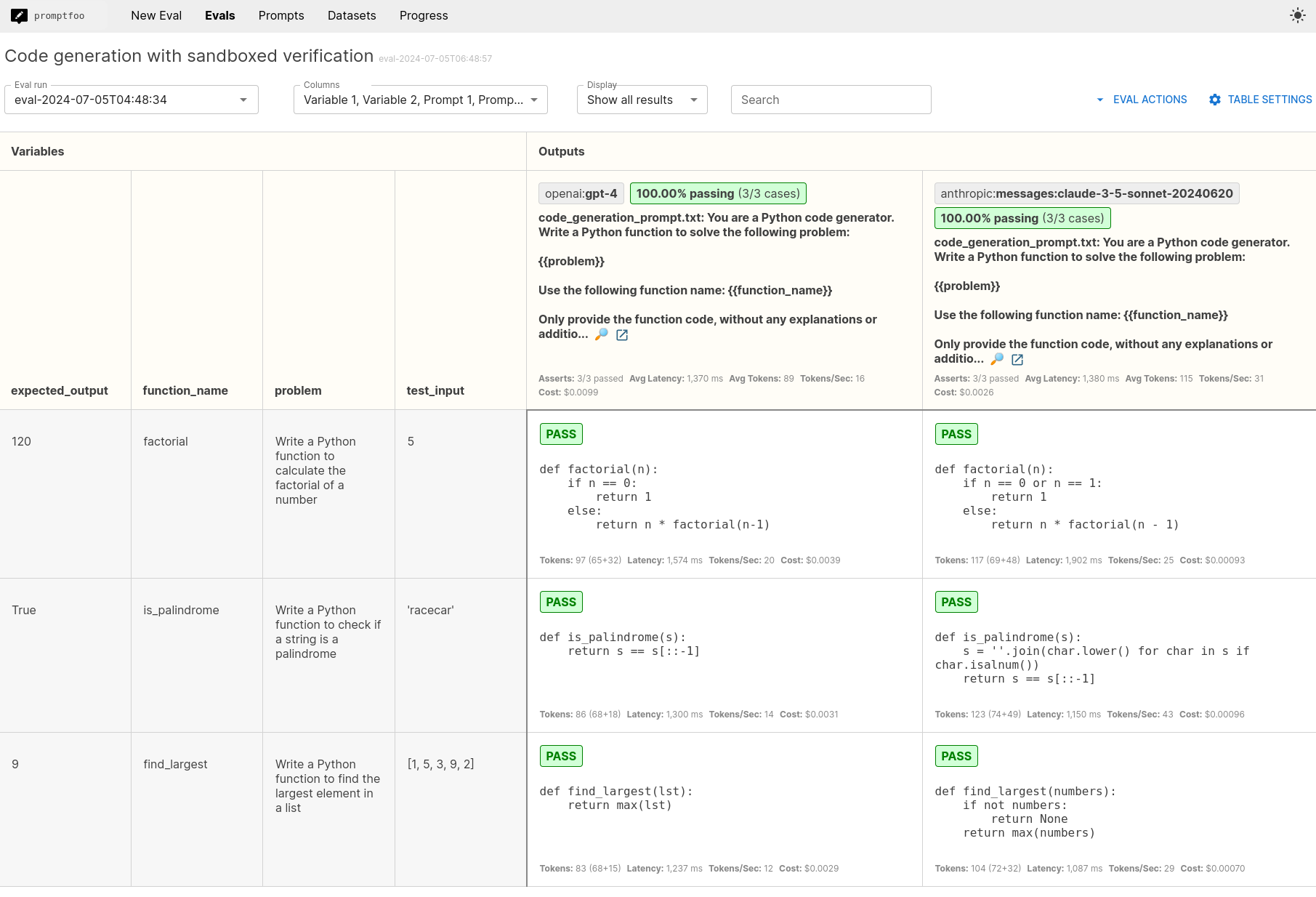
Analyzing Results
After running the evaluation, open the web viewer:
promptfoo view
This will display a summary of the results. You can analyze:
- Overall pass rate of the generated code
- Specific test cases where the LLM succeeded or failed
- Error messages or incorrect outputs for failed tests
What's next
To further explore promptfoo's capabilities, consider:
- Testing different LLM providers
- Modify your prompt
- Expanding the range of coding problems and test cases
For more information, refer to the official guide. You can also explore continuous integration and integrations with other tools.